Below are tabs with more information about Dr. Borrett's teaching and courses.
- Schedule
- Survey of Biological Research
- Network Science
- Ecology Lecture
- Ecology Lab
- Ecological Modeling Lecture
- Ecological Modeling Lab
- Ecological Thought
- Systems Ecology
- SEEL Meetings
- Research Students
- Advising
- ENA Workshops
Borrett Teaching Statement (updated 1/3/2010)
Past Courses
• Ecology. UNCW Bio366
• Ecology Laboratory. UNCW Biol366
• Bringing Home the Biosphere. UNCW Bio495
• Fundamentals of Ecological Modelling. UNCW BIO534 & BIOL534
• Ecological Thought: Past to Present. UNCW BIO602
• Systems Ecology and Ecological Network Analysis. UNCW Su 2011, Beijing Normal University Su13
• Ecological Network Analysis
May 2023 @ ISEM2023. Here is a link to the workshop materials
May 2016 @ ISEM2016. Here is a link to the workshop materials
August 2015 @ ESA (#esa100). Here is a link to the workshop materials.
March 2011 @ Northern Arizona University: Workshop: Introduction to Ecological Network Analysis
• R Tutorial (with Matt Lau). UNCW Su2011
-
UNCW R Tutorial Notes by Matt Lau @NAU
-
Additional R Resources: CRAN, Kickstarting R, Addicted to R
-
Example: Forest Data, Forest Analysis1
• 2006. Stanford University. Fundamentals of Ecological Modeling. Undergraduate and graduate course. Co-instructor: K.R. Arrigo. Stanford, CA.
• 2003. Institute of Ecology. Ecological Thought: Past to Present. Required course for ecology graduate students. Co-instructors: B.C. Patten, S.J. Whipple. Athens, GA. syllabus
• 2003. Skidaway Institute of Oceanography. Ecosystem Complexity in the Marine Environment – Seeking an Answer to the Question: What is Biocomplexity? Three week short course for undergraduate and graduate students. Co-instructors: P.G. Verity, M.E. Frischer, B.C. Patten, S.J. Whipple. Skidaway, GA.
• Guest Lecturer and Teaching Assistant. 2002. Institute of Ecology. Theory of Systems Ecology. Graduate course. Professor: B.C. Patten. Athens, GA.
Fall 2013
Biological Resources |
Schedule
# |
Date |
Topic/Activity |
Reading |
Assignment Due |
| 1 | 8/26 |
Course Introduction (notes) |
||
9/2 |
Labor Day - no class |
|||
| 2 | 9/9 |
Dr. Finelli, Chair Dept. Biology and Mairne Biology (notes) |
||
| 3 | 9/16 |
Business of Science (notes) |
research synopsis |
|
4 |
9/23 |
Dr. Frampton, Virology (Meet in Dobo Hall 110) |
||
5 |
9/30 |
research synopsis
|
||
6 |
10/7 |
Dr. Rhodes, Microbiology (notes) |
research synopsis
|
|
7 |
10/14 |
research synopsis
|
||
8 |
10/21 |
Dr. Arbogast, Mammology & Wild Sumaco Wildlife Sanctuary (Ecuador) |
research synopsis
|
|
9 |
10/28 |
research synopsis
|
||
10 |
11/4 |
Dr. Wilbur, CMS Oyster Hatchery meet at Center for Marine Science |
research synopsis
|
|
| 11 | 11/11 |
Dr. Pyott, Physiology |
|
research synopsis
|
| 12 | 11/18 |
research synopsis
|
||
| 13 | 11/25 |
Dr. Brander, Ecotoxicology |
research synopsis
|
|
14 |
12/2 |
Dr. Taylor, Tour Microscope Facility (meet in Dobo 131) |
research synopsis
|
|
1 hour seminar, Fall 2015
Description
We are linked through a myriad of networks. Google lets us search the World Wide Web of information, Facebook helps us stay in touch with friends, and LinkedIn promises to help us find jobs. We use
transportation networks to move ourselves and goods, power grids to distribute our power, and even our language can be bound into web like word clouds. Darwin recognized the tangled webs of life that are
central to evolution by natural selection. In this interdisciplinary honors course, students will discover the emerging area of network science. Students will explore the diversity of networks in our social, technological, and natural world, and learn about tools to model and analyze them. Upon completion, successful students will be able to identify and describe network patterns common in complex systems, along with their relative weaknesses and strenghts.
Reading Discussions |
Schedule
| C# | Date | Subject | Materials | Homework | |
| 1 | 24 Aug |
Introduction to Networks (notes) |
Required Manuel Lima: A visual history of human knowledge Recommended Eric Berlow: Simplifying complexity (TED ~4 min) |
Homework 1 (Due C#2)
|
|
| 2 | 31 Aug | Network Foundations 1 (notes) |
Required Barabasi 2012 Network Takeover. Science Recommended Clay Shirky: How the Internet will (one day) transform government (TED ~ 20 min) Digital Footprint | Michelle Clark (TEDx)
|
Homework 2 (Due C#3) | |
| 7 Sept | Labor Day - No Class | ||||
| 3 | 14 Sept | Network Foundations 2 (notes) |
Required Watts & Strogatz (1998) Small Worlds Barabasi (2008) Scale Free Networks Recommended Eric Berlow and Sean Gourley: Mapping ideas worth spreading Rachel Botsman: The currency of the new economy is trust |
Homework 3 (Due C#4) | |
| 4 | 21 Sept | Guest Lecture - David Hines | |||
| 5 | 28 Sept | Network Foundations 3 | Required none |
Reading Proposals (Due C#5) |
|
| 6 | 5 Oct | Rain Day | |||
| 12 Oct | Fall Break | ||||
| 7 | 19 Oct | Guest Lecture - Lisa Hollenshead | Required Jacoby et al 2012. Developing a deeper understanding of animal movements and spatial dynamics through novel application of network analyses Recommended |
||
| 8 | 26 Oct | Discussion Leader is Jordan Ormand Foster |
Liu et al. 2008. Disrupted small world networks in schizophrenia. | Homework 4 (Due C#9) | |
| 9 | 2 Nov | Discussion Leader is Aysha Khan |
Brewer et al. 2011. Meditation experience is associated with differences in default mode network activity and connectivity. | ||
| 10 | 9 Nov | Discussion Leader is Chrysanthi Siarkas |
Osgood et al. 2013. Peers and the emergence of alcohol use: Influence and selection processes in adolescent friendship networks. | ||
| 11 | 16 Nov | Discussion Leader is Danielle DuBois
|
Warschauer 2007. The paradoxical future of digital learning |
|
|
| 12 | 23 Nov | Discussion Leader is Mary Benton |
Dunbar et al. 2015. The structure of online social networks mirrors those in the offline world |
Homework 5 (Due C#12) Write a ~1 page essay that compares and contrasts the network models and anlyses presented in two of the papers we have read in class. |
|
| 13 | 30 Nov |
|
|||
| 3 Dec | Reading Day | ||||
Other Resources
Papers |
Websites |
Brandes et al 2013 What is Network Science? Network Science |
Journal of Complex Networks |
| Proloux et al. 2005. Network thinking in ecology and evolution. TREE | Network Science Journal |
| Borrett et al. 2014. The rise of Network Ecology: Maps of the topic diversity and scientific collaboration. Ecol. Model. | Visual Complexity |
| Mark Newman | |
| EcoNet Website | |
| How Google makes improvements to its seach algorithm | |
| Digital Footprint Video (ok, not great) |
Summer 2018
|
|
Required Resources 1. Smith and Smith (2015) Elements of Ecology (9th edition). Pearson Ed. 2. TurningPoint Cloud Account, current Subscription, & a Response Device |
Additional Useful Information
|
||
Participation A TurningPoint Cloud Account and a response device are requried for this class. Student Registration Instructions (via Blackboard) Progress (6/7/2018) |
Assignments
|
|||
 |
||||
Schedule
# |
Date |
Topic |
Readings/Assignments Due |
I. Introduction |
|||
1 |
16 May | Reading
EcoPhoto Project Suggested Resources The Study Cycle | LSU Center for Academic Success (video, 3:15 min) The Secete Life of a Raindrop | KQED QUEST Video (~10 min) Thermal Delight | 99% Invisible Podcast
|
|
II. Individuals |
|||
2 |
17 May | Individual Organisms: Niches, Conditions, and Resources (preview, notes, participation ) |
Reading Participation
EcoPhoto Project
Suggested The Upside of the Bitter Cold: It Kills Bugs that Kill Trees | NPR, 2014 |
3 |
21 May | Physiological Ecology of Plants and Animals (preview, notes, participation) |
Reading
EcoPhoto Project
Suggested
|
4 |
22 May | continued | |
| 5 | 23 May | Life History (preview, notes) | Reading/Homework
Exam Preparation Activity
|
| 6 | 24 May | EXAM I (Scores) | EcoPhoto Project
|
III. Populations |
|||
| 7 | 29 May | Ecological Populations (participation) |
Reading
EcoPhoto Project
|
| 8 | 30 May | Population Gowth (preview, notes) Population Regulation & Intraspecific Competition (preview, notes) |
Reading
|
| IV. Interactions | |||
9 |
31 May |
Interspecific Competition (preview, notes, participation) |
Reading
Modeling Homework Suggested
|
10 |
4 June |
Predation (preview, notes, participation) |
Required
Modeling Homework EcoPhoto Project
|
| 11 | 5 June
|
Symbiosis, Parasitism, Mutualisms (preview, notes, participation) |
Reading
Suggested
|
V. Communities |
|||
12 |
6 June | Community Structure (preview1, preview2, notes)
|
Reading
Exam Prepartation Activity
Suggested
|
| 13 | 7 June | EXAM II (Scores, Discussion) | |
| VI. Ecosystems | |||
| 14 | 11 June | Community Dynamics (preview, notes) Ecosystem Energetics and Organization (preview, notes, participation) |
Reading
EcoPhoto Project
Suggested |
| 15 | 12 June
|
Ecosystem Energetics and Organization (continued, participation) |
Reading
|
| 16 | 13 June | Decomposition and Nutrient Cycling (preview, notes) Biogeochemical Cycling: Part I (preview) & Part 2 (preview) - notes |
Reading
Suggested
|
| VIII. Conclusions | |||
| 17 | 14 June | Wrap Up (participation) Part 1: Ecological Address of the Lower Cape Fear (notes) Part 2: Ten+ Fundamental Principles of Ecology (notes)
|
Exam Preparation Activity
EcoPhoto Project
Suggested
|
| 15 June | Reading Day | ||
18 |
18 June | EXAM III (8-11 am, scores) |
|
Interesting Ecology Videos
Conserving the Canopy http://www.ted.com/talks/nalini_nadkani_on_conserving_the_canopy.html
Mate selection in Birds of Paradise (http://www.youtube.com/watch?v=6gAxbxxmYZ8)
Human Microbiome (https://www.youtube.com/watch?v=5DTrENdWvvM)
Trophic Cascade Video (Wolves in Yellowstone)
PBS: Secrets of the Longleaf Pine (video, 56:47)
Summer 2018
Laboratory Report Resources Laboratory Report Instructions Short Report Grading Rubic (Excel) Full Report Grading Rubric (Excel) How to (seriously) read a scientific paper Why can't college graduates write coherent prose? | Washington Post Op-Ed by Jeffrey J. Selingo (Aug 2017)
|
|
 |
 |
Schedule
Description of the laboratories and their assignment directions are in the class laboratory manual.
Lab# |
Week |
Topic |
Readings & Assignments |
1 |
May 17 |
Describing a Population (notes) | Questions Due in Class
see Lab Description (bring printed copy of pages 18-20 to class) |
2 |
May 22 |
Sampling Sedentary Organisms (notes) |
Short Lab Report (Due Lab 3)
|
3 |
May 24 |
Population Dispersion and Association (notes) |
Required Short Lab Report (Due Lab 4) Recommended Resources
|
| Forest Ecology Laboratory (next 3 labs) | |||
 |
Forest Ecology Laboratory Report Draft Laboratory Report (Due Lab 6) Revised Laboratory Report (Due Lab 8) Laboratory Report Instructions Link to Common Copy Editing Marks |
||
| 4 | May 29 | Forest Ecology I: Hypothesis development and sampling design (notes) |
|
| 5 | May 31 | Forest Ecology II: Sampling
|
Enter the data collected into Excel file & email file to all team members. |
| 6 | June 5 | Forest Ecology III: Data Analysis (notes) |
Pechenik, Chapters 4 & 5 Examples: Forest Data, Forest Analysis1, data in Excel format |
| 7 | June 7 | Wetland Communities (notes)
|
Questions and graph due in class. Recommended NATURALIST’S NOTEBOOK: CAROLINA BAYS: Another Man’s Treasure |
| 8 | June 8 | Writer's Workshop -- Revising your Forest ecology Laboratory Reprots |
Porcher et al. 2018. Fire- and distance dependent recuritment of the Brazil nut in the Peruvian Amazon. Forest Ecology and Management 427: 52–59 |
9 |
June 14 | Laboratory Final Exam | |
Recommended Activity Visit the Land of the Longleaf Pine exhibit at the Cape Fear Museum of Science and History at 814 Market Street in Wilmington (closed on Monday). |
|||
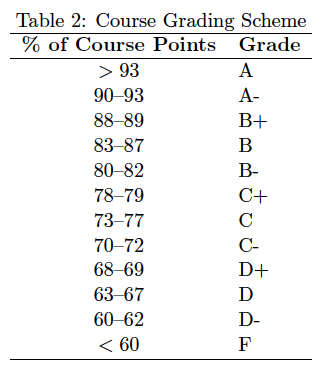
Grading Scheme
Related Links
Land of the Long Leaf Pines Exhibit @ Cape Fear Museum of Science and History
Cape Fear Estuary: From River to Sea
BIO 534 :: Advanced Ecology :: Fundamentals of Ecological Modeling
Fall 2017
Schedule
# |
Date |
Topic |
Reading |
Homework (due date) |
Introduction |
||||
1 |
Aug. 16 |
Introduction (notes) |
H1: Mangel 2006 Math Warm Up (Due Aug. 22) :: (solution) | |
2 |
21 |
Models and Science (notes) |
Required West Wing Clip - Gall Peters Projection (4 min YouTube Clip) Suggested America's Last Top Model (20 min podcast) | 99% Invisible
|
H2: Model ID Assignment (Due Aug. 23) |
3 |
23 |
Art of Modelling (notes) |
|
|
4 |
28 |
System Conceptualization (notes) |
Patten & Van Dyne (pers.com); FEM Ch4 |
H3: Conceptualization (due Aug 30) |
5 |
30 |
Single State Variables Models: Bathtubs and Populations (notes) |
Gotelli Ch1 |
H4: Problem Set - Gotelli problems 1.2 & 1.3 (due Sept. 14) |
Quantitative Modeling |
||||
Sept.4 |
||||
6 |
6 | Exam 1 - Take Home | ||
7 |
11 |
Population Regulation and Intraspecific Competition: Logistic Growth (notes) |
Gotelli Ch2 |
H5: Problem Set - Gotelli problems 2.1, 2.2, & 2.3 (due Sept. 25) |
8 |
13 |
Structured Population Models
(notes, Life Tables Example, Leslie Matrix Analysis example in R) |
Gotelli Ch3 | H6: Problem Set - Gotelli problem 3.2 (due Sept. 25) |
| 9 | 18 | Populations in Space (notes) | Stevens Ch4 | H7: Problem Set - Stevens 4.1. (due Sept. 25); Stevens 4.2 is a challenge problem. |
| 10 | 20 | Interspecific Competition (notes) | Gotelli Ch5 |
H8: Problem Set - Gotelli problems 5.1 & 5.2 (due Sept. 25) |
| 11 | 25 |
Collaborative Problem Set Review & Discussion: Anway | ||
| 12 | 27 | Case Study: Guest Lecture: Long | ||
| 13 | Oct 2 |
Case Study: Guest Lecture: Cheripka | ||
| 14 | 4 |
Work in Teams (~2) to complete the "Homework" activity in prepariation for the Mutualism activity | H9: Activity for Mutualism (due Oct 11) | |
5-6 |
Fall Break | |||
| 15 | 9 |
Predation (notes) | Gotelli Ch 6 | H10: Problem Set - Gotelli problems 6.1 & 6.2 (due Oct. 11)
|
| 16 | 11 |
Mutualisms (notes) |
|
|
| 17 | 16 | Three State Varables: Chains & Webs (notes; show) | (start reading DMB Ch9 for next class) | |
| 18 | 18 |
Environmental Forcing, Parameterization, and Calibration (notes) |
||
Model Evaluation |
||||
| 19 | 23 |
Discussion: Confronting Models with Data | Fussman et al. 2000: Shertzer et al. 2002 | Reading Proposals Due (assignment, proposals) |
| 20 | 25 | Discussion: Model Evaluation | Required Oreskes 1994; Schmolke et al 2010 Suggested Spherical Horses & Frictionless Wheels | Engines of our Ingenuity, Podcast 2334 |
|
| 21 | 30 |
Model Analysis: Sensitivity Analysis (notes) |
Murdoch et al. 2013 | |
| 22 | Nov 1 |
Exam 2 - Take Home | ||
Case Studies |
||||
| 23 | 6 | Network Ecology (notes) | ||
| 24 | 8 |
Hansen, A.N., Visser, A.W., 2016. Carbon export by vertically migrating zooplankton: an optimal behavior model. Limnology and Oceanography 61, 701-710.
|
Jacie |
The Dreaded Discussion: Ten Ways to Start | Frederick
|
| 25 | 13 |
Raatz, M., Gaedke, U., and Wacker, A. 2017. High food quality of prey lowers its risk of extinction. Oikos 126: 1501 – 1510
|
David |
|
| 26 | 15 |
Marn N, Jusup M, Legović T, Kooijman SALM, Klanjšček T. 2017. Environmental effects on growth, reproduction, and life-history traits of loggerhead turtles. Ecological Modelling 360:163-178.
|
Tiffany |
|
| 27 | 20 |
Holland, J. N., & Deangelis, D. L. (2010). A consumer-resource approach to the density-dependent population dynamics of mutualism. Ecology, 91(5), 1286-1295.
|
Amanda |
|
22-24 |
Thanksgiving | |||
| 28 | 27 |
Hopf, J. K., Jones, G. P., Williamson, D. H. and Connolly, S. R. (2016). Fishery consequences of marine reserves: short-term pain for longer-term gain. Ecol Appl, 26: 818–829. doi:10.1890/15-0348
|
Danielle |
|
| 29 | 29 |
Summary & Conclusions | ||
Dec 1 |
Reading Day |
|||
Dec 4 |
Final Exam Time - 11:30-2:30 | |||
Additional Resources
SPHERICAL HORSES & FRICTIONLESS WHEELS, Engines of our Ingenuity Podcast 2334
The Scale of Nature: Modeling the Mississippi River | K.D. Cheramie, March 2011
BIOL 534 | Advanced Ecology Laboratory | Fundamentals of Ecological Modeling
Fall 2016
Teaching Project Description (Comming Soon) |
Schedule
| Date | Topic | Resources | Due Date | Solutions |
| Aug 16 | Getting Started with R (notes) Please do the following: 1. Download and install R on your computer (CRAN). 2. Open R and play with it. 3. Start Lab 1: Introduction to R for Ecological Modeling from Dr. Ben Bolker's website. The following exercises will be due at the end of the next lab period: {2.1, 3.1, 5.1, 5.2, 5.3, 5.4, 8.2, 8.3, 8.4, 8.5, 8.6, 9.2} 4. Explore these resources |
Emacs; Tinn-R; Information about other text editors for R is here; DATA |
exercises due Lab 2. | (Solutions) |
| 23 | Lab 2: Practical Programming (notes) |
Recommended Reading |
end of lab | (Solutions) |
| 30 | Lab 3: Single State Variable Models: Exponental Growth & Logistic Growth (notes)
|
Shiflet & Shiflet 2006 Module 5: simulation techniques |
Sept. 13 |
(Solutions) |
| Sept. 6 | Lab 3: ...continued | |||
| 13 | Lab 4: Ricker Model & Chaotic Dynamics | Otto&Day-chaos; optional May 1974 | Sept. 20 | (Solution) |
| 20 | Lab 5: Two State Variable Models: Resource-Consumer Models | Control Fuction Notes | Oct. 11
|
(Solution) |
| Sept. 27 | Lab 5: ...continued | |||
| Oct. 4 | Teaching Ecological Modelling Project (Part 1): a. Learn to use R Shiny package to create Web Apps b. Work in teams (2-3 students) to create a web app that an undergraduate studnet could use to investigate the dynamics of the Logistic growth model. Use sliders as inputs for the model parameters and initail popuation sizes. |
Building Shiny apps -- an ineractive tutorial Creating interactive data visualizations using Shinny App in R |
||
| Oct. 11 | Teaching Ecological Modelling Project (Part 2): Create Ecological Modelling Learning Modules for the BIO366 studnets. | |||
| 18 | Lab 6: Three State Variable Models: Chains and Webs | Beisner et al. 2003 |
|
(Solution) |
| Oct 25 | Lab 6: ...continued | Research Project Topic Selection Due | ||
| Nov 1. | Lab 7: Connecting Models and Data | no report due | ||
| 8 | Work on Course Projects | |||
| 15 | Work on Course Projects | Teaching Projects Due | ||
| 22 | THANKSGIVING HOLIDAY | |||
| Nov 29 | Work on Course Projects | Research Project Reports Due (5 pm) | ||
| Dec 4 | Project Presentations (Final Exam Period Lab: 3-6 pm) |
Research Project Presentations Due |
||
R Programming Help, Tutorials, & Advice
There are lots of R programming resources on the web. I am collecting a few more useful resources here.
A plea for consistent style! | http://sas-and-r.blogspot.com -- Style guides for writing more readable code.
Google's R Style Guide | Google -- Style guides for writing more readable code.
Functional Programmin via Cupcakes | Stanley Wickham -- Wickham is arguing that we should replace many for-loops with functions. I learned two additional elments: the seq_along() function and the purr library.
R Tutorial for Beginners: A Quick Start-Up Kit | Mitchell A. Sanders -- this is a very terse introduction that assumes a bit of knowledge about computer programming.
R Reference Card | CRAN R-Project
An Introduction to R | CRAN R-Project -- this is a very helpful resource for beginning R coding.
R-bloggers | R news and tutorial site.
-- Mastering R Plot | Part 1 Colors, Legends, & Lines | Part 2 Axes | Part 3 Outer Margins
Presentation Resources
Here are links to several sources of advice on making and giving high quality presentations
Life After Death by PowerPoint | Don McMillan
Death by PowerPoint | Alexei Kapterev
How to avoid death By PowerPoint | David JP Phillips
The Cognitive Style of PowerPoint | Edward Tufte
Spring 2011 Schedule
Date
|
Topic
|
Readings
|
Exercises
|
13 Jan |
No class |
||
18 |
Introductions |
sign up for topics |
|
20 |
Scientific Origins |
A. Kormondy (TOC; Introduction; Early Natural History) |
|
25 |
Ecological Stoichiometry |
A. Kormondy (Physical & Chemical Environment - Liebig, Blackman, Shelford) B. Reiners 1986 |
|
27 |
D. Hillebrand, Helmut; Gamfeldt, Lars; Jonsson, Per R; Matthiesen, Bert. 2009. Consumer diversity indirectly changes prey nutrient content. Mar Ecol Prog Ser 380:33-41 (link) |
||
Feb 1 |
Biosphere and Gaia |
||
3 |
Ex. 1 Due |
||
8 |
Density Dependence |
A. Kormondy (Populations - Malthus, Verhulst, Birch, Nicholson, Hairston et al.) |
Exercise 2: Propositional Logic |
10 |
C.
Filin, I, Holt, RD, andl Barfield, M. 2008. The Relation of Density Regulation to Habitat Specialization, Evolution of a Species’ Range, and the Dynamics of Biological Invasions.
A link to the paper is: |
||
15 |
Host-Parasite Interactions |
A. Kormondy (Populations: Burkholder, Gause, Connell, Wheeler) B. May 1983 |
|
17 |
C. TBD |
Ex. 2 Due |
|
22 |
Biodiversity and Ecosystem Fcn |
||
24 |
C. TBD |
||
Mar 1 |
Community Assembly |
A. Kormondy (Community - Clements, Braun-Blanquet and Furrer, Ramensky, Gleason) |
|
3 |
C. TBD |
||
8 |
Niche vs. Neutral Theory |
B. Hubbell 2005 |
Exercise 3. 10 Fundamental Principles
|
10 |
D. TBD |
||
15 |
Spring Break | ||
17 |
Spring Break | ||
22 |
Ecosystem Energetics |
A. Kormondy (ecosystems - Evans, Transeau, Juday, Lindeman, Clarke, Odum) |
|
24 |
|||
29 |
Topic A to be selected |
||
31 |
|||
April 5 |
Topic B to be selected |
||
7 |
|||
12 |
Topic C to be selected |
||
14 |
|||
19 |
Fundamental Processes pt 1 |
||
21 |
Easter Break |
||
26 |
Fundamental Processes pt 2 | Scheiner and Willig 2008 | |
28 |
Summary and Discussion |
Reflection Paper Due |
|
14-May |
Commencement |
||
Topic Proposals
Systems Ecology :: Summer 2013
This course was co-taught with Dr. John Schramski (UGA) at Beijing Normal University
Course Resources
Software for Ecological Network Analysis
EcoNet |
EcoNet (online tool) |
enaR: R package |
enaR is a professional grade tool for ecological network analysis. It is a package of functions for R that builds on the network and social network analysis packages created by Carter Butts. You can download the software from CRAN. Simple enaR Tutorial (illustrated example of use with the Cone Springs model) Vignette (shows how to use software) Borrett & Lau 2012, EcoSummit Presentation Introducing enaR (ppt) enaR Reference Card (short list of primary commands) Example Code (batch_example.r, edge_deletion_ENA_sensitivity.r, sa_example.r) SCOR formatted data files for examples (neuse_2.dat, neuse_3.dat, neuse_4.dat, neuse_5.dat, avgLanier.dat) |
Lecture Notes
Dr. Borrett's Notes |
Additional Resources Online |
Albert Norström explains the basics of systems ecology thinking (YouTube) |
Systems Ecology Graduate Program (University of Montana) |
Systems Ecology and Ecological Engineering (University of Florida) |
Systems Ecology Program (University of Maryland) |
Spring 2015
We are meeting Tuesday's at 12:30 pm in the SEE Lab Space. Please join us to disucss current topics and research in Systems Ecology and Ecoinformatics.
Invitation
Dr. Borrett is always looking for hardworking and intellectually curious studnets to join the SEE Laboratory's journey of scientific discovery. Studnets can work in the lab at all levels: undergraduate Directed Independnet Studies, honors projects, masters thesis, and PhD disertations. If you are considering joining the lab, please peruse this website and read a few of our recent publications to develop a better understanding of our work. While the scope of our research can be quite broad, I recommend you start with this encyclopedia entry on Network Ecology as much of our work falls in this domain. If this work interests you, please contact Dr. Borrett directly (borretts {@} uncw.edu).
Resources
I am listing a few resources here that new and older studnets may find useful.
Journey into the Unknown, Brian Greene discussess the journey that is science.
Simplfying Complexity, TED talk by Eric Berlow about using network science to undersatand complex systems. In an interesting follow up talk, Dr. Berlow and Sean Gourley illustrate Mapping Ideas Worth Spreading.
Expectations
This page is still under construction, but here are a few guiding principles.
"We write to think, not think to write" Bart Dredge @Austin College. A corrolary of this principle is that unclear writing is evidence of unclear thinking.
Science is a community activity. We publish our work so that it can contribute to the protracted discourse that is science discovery and knowledge construction. Given this position, science does not really exist until it is publically available -- until its published in some form.
All studnets are expected to participate in scheduled laboratory meetings.
DIS
Honors
Masters
PhD
This tab is a collection of resources for academic advising at UNCW.
General
Here are some general resources for students.
Apps for Students (courtesey of UNCW CHHS)
Internships
Guidelines for Internships at UNCW
Internship information from the UNCW Career Center. This site includes links to the necessary forms.
| For Credit Internships (in Biology) | |
| Regular Semester | Summer Semester |
3 hrs work/ week = 1 credit hour 6 hrs/ week = 2 credit hours 9 hrs/ week = 3 credit hours |
One Session Enrollment: 12 hrs/ week = 1 credit Two Session Enrollment: 6 hrs/ week = 1 credit |
Courses
There are lots of interesting and useful courses at taught at UNCW. This is a list of courses that I recommend for biology and marine biology majors who are looking for challenging, interesting, and perhaps useful courses outside of the normal track.
| Undergraduate | Graduate |
Practicing Science
Scientists Have No Defense Against Awe | Choudhry @ Nautilus 2016
The Mistrust of Science | A Gawande @ The New Yorker 2016
Miscellaneous: Teaching, Learning, Communicating
Advice on writing emails to professors.
Dr. Borrett has taught a number of short workshops or tutorials on Ecological Network Analysis. Here are links to the workshop pages and course materials
Simple enaR Tutorial (illustrated example of use with the Cone Springs model)
2023 May. @ISEM 2023. Ecological Network Analysis Tutorial. Taught with Brian Fath.
2019 October. @ISEM 2019 Ecological Network Analysis Tutorial. Taught with Brian Fath, Ursula Scharler, and Caner Kazanci
2016 September. @ECSA56. Ecological Network Analysis Tutorial
2016 May. @International Society for Ecological Modelling. Introduction to Ecological Network Analysis
2015 August. @Ecological Society of America. Introduction to Ecological Network Analysis
2011 March @ Northern Arizona University: Workshop: Introduction to Ecological Network Analysis