PSY 555 Homework 13
Answers
Chapter 9: #1,2,3,5,6,7,8
9.1.†††††
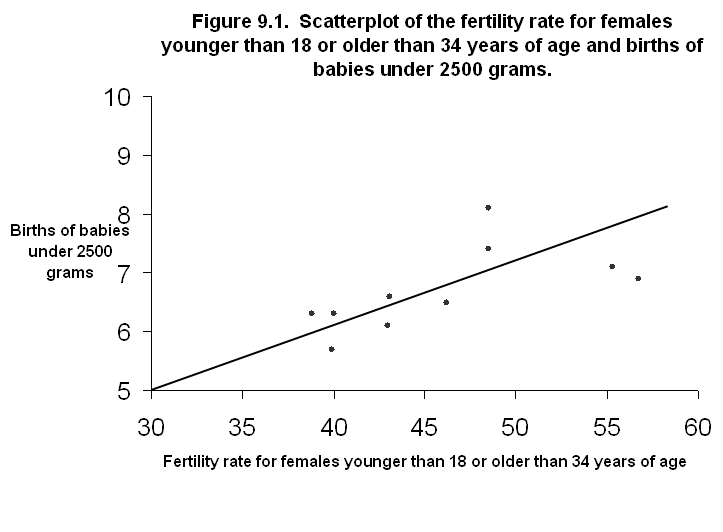
9.2.†††††
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
6.1 |
43.0 |
-.6 |
.36 |
-3 |
9 |
1.8 |
|
7.1 |
55.3 |
.4 |
.16 |
9.3 |
86.49 |
3.72 |
|
7.4 |
48.5 |
.7 |
.49 |
2.5 |
6.25 |
1.75 |
|
6.3 |
38.8 |
-.4 |
.16 |
-7.2 |
51.84 |
2.88 |
|
6.5 |
46.2 |
-.2 |
.04 |
.2 |
.04 |
-.04 |
|
5.7 |
39.9 |
-1 |
1 |
-6.1 |
37.21 |
6.1 |
|
6.6 |
43.1 |
-.1 |
.01 |
-2.9 |
8.41 |
.29 |
|
8.1 |
48.5 |
1.4 |
1.96 |
2.5 |
6.25 |
3.5 |
|
6.3 |
40.0 |
-.4 |
.16 |
-6 |
36 |
2.4 |
|
6.9 |
56.7 |
.2 |
.04 |
10.7 |
114.49 |
2.14 |
![]() †
†![]() †††
††† ![]() †
† ![]() †
†![]()
![]() =24.54
=24.54
![]() †† †
†† † ![]() ††††
†††† ![]()
![]()
![]()
![]()
![]()
![]()
![]()
9.3.††††† For Y values please refer to 9.2.
|
|
|
|
|
|
9.2 |
-1.05 |
1.1025 |
.63 |
|
12.0 |
1.75 |
3.0625 |
.7 |
|
10.4 |
.15 |
.0225 |
.105 |
|
9.8 |
-.45 |
.2025 |
.18 |
|
9.8 |
-.45 |
.2025 |
.09 |
|
7.7 |
-2.55 |
6.5025 |
2.55 |
|
10.9 |
.65 |
.4225 |
-.065 |
|
9.5 |
-.75 |
.5625 |
-1.05 |
|
11.6 |
1.35 |
1.8225 |
-.54 |
|
11.6 |
1.35 |
1.8225 |
.27 |
![]() †††
††† ![]() ††††
††††![]() =2.87
=2.87
![]()
![]()
![]()
![]()
![]()
9.5.
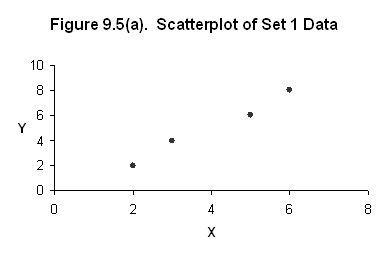
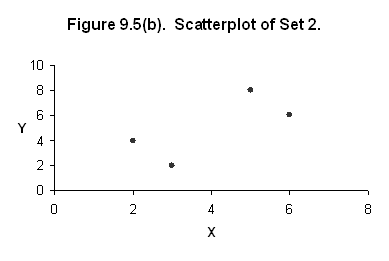
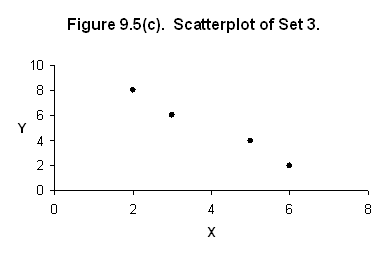
9.6.
Set 1:
|
X |
Y |
|
|
|
|
2 |
2 |
-2 |
-3 |
6 |
|
3 |
4 |
-1 |
-1 |
1 |
|
5 |
6 |
1 |
1 |
1 |
|
6 |
8 |
2 |
3 |
6 |
†††††† ![]() †††††††
†††††††![]() ††††††††††††††††††††††††
†††††††††††††††††††††††† ![]()
![]() † †
† † ![]()
![]()
Set 2:
|
X |
Y |
|
|
|
|
2 |
4 |
-2 |
-1 |
2 |
|
3 |
2 |
-1 |
-3 |
3 |
|
5 |
8 |
1 |
3 |
3 |
|
6 |
6 |
2 |
1 |
2 |
![]() †† †
†† † ![]() ††††††††††††††††††††††††
†††††††††††††††††††††††† ![]()
![]() † †
† † ![]()
![]()
Set 3:
|
X |
Y |
|
|
|
|
2 |
8 |
-2 |
3 |
-6 |
|
3 |
6 |
-1 |
1 |
-1 |
|
5 |
4 |
1 |
-1 |
-1 |
|
6 |
2 |
2 |
-3 |
-6 |
![]() †† †
†† † ![]() ††††††††††††††††††††††††
†††††††††††††††††††††††† ![]()
![]() † †
† † ![]()
![]()
9.7.
Set 1:
|
|
|
4 |
|
1 |
|
1 |
|
4 |
![]()
![]()
Set 2:
|
|
|
4 |
|
1 |
|
1 |
|
4 |
![]()
![]()
Set 3:
|
|
|
4 |
|
1 |
|
1 |
|
4 |
![]()
![]()
Set 1:
|
|
|
9 |
|
1 |
|
1 |
|
9 |
![]()
![]()
Set 2:
|
|
|
1 |
|
9 |
|
9 |
|
1 |
![]()
![]()
Set 3:
|
|
|
9 |
|
1 |
|
1 |
|
9 |
![]()
![]()
![]()
Set 1:† ![]()
![]()
Set 2:† ![]()
![]()
Set 3:† ![]()
![]()
9.7(b).†† Three
arrangements of Y will result in the lower possible positive correlation:
2
8 6 4 or 6 4 2 8 or 6 2 8 4†††† [r=.14]† [See example below]
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
2 |
6 |
-2 |
4 |
1 |
1 |
-2 |
|
3 |
2 |
-1 |
1 |
-3 |
9 |
3 |
|
5 |
8 |
1 |
1 |
3 |
9 |
3 |
|
6 |
4 |
2 |
4 |
-1 |
1 |
-2 |
![]() †
†![]() ††††
†††† ![]() ††
†† ![]() †† †
†† †![]()
![]() =2
=2
![]() ††
†† ![]() †††
††† ![]()
![]()
![]()
![]()
![]()
![]()
9.8.
Yes.† While technically it would not be appropriate
to do a correlation in the presence of curvilinearity (due to the assumption of
linearity for Pearsonís r), the coefficient (r) would still tell you how well a
straight line fits, even if you think that a curved line would fit better.† Often the fit of a straight line is
sufficiently good for our purposes.†
However, it is important to note that by using a linear relation with
curvilinear data, you will underestimate the relation.
1.
You use
a correlation when you have standardized your data and we are attempting to
describe the degree to which two variables are related.† If we have raw data and we want to predict
some outcome, regression equations are more appropriate.
2.††††††† -1.0, .99,-.97,.87,-.85,.66,.55,.43,-.34,.28,-.24,-.12,-.11,-.02,.01
3.††††††† The
criterion variable is the variable that you want to predict (akin to a
dependent variable).† The predictor
variable is the variable that is being utilized to predict the criterion
variable (akin to the independent variable).